In the last months, I’ve learned a lot about Vue. From building SEO-friendly SPAs to crafting killer blogs or playing with transitions and animations, I’ve experimented with the framework thoroughly.
But there’s been a missing piece throughout my learning: plugins.
Most folks working with Vue have either comes to rely on plugins as part of their workflow or will certainly cross paths with plugins somewhere down the road. Whatever the case, they’re a great way to leverage existing code without having to constantly write from scratch.
Many of you have likely used jQuery and are accustomed to using (or making!) plugins to create anything from carousels and modals to responsive videos and type. We’re basically talking about the same thing here with Vue plugins.
So, you want to make one? I’m going to assume you’re nodding your head so we can get our hands dirty together with a step-by-step guide for writing a custom Vue plugin.
First, a little context…

Plugins aren’t something specific to Vue and — just like jQuery — you’ll find that there’s a wide variety of plugins that do many different things. By definition, they indicate that an interface is provided to allow for extensibility.
Brass tax: they’re a way to plug global features into an app and extend them for your use.
The Vue documentation covers plugins in great detail and provides an excellent list of broad categories that plugins generally fall into:
- Add some global methods or properties.
- Add one or more global assets: directives/filters/transitions etc.
- Add some component options by global mixin.
- Add some Vue instance methods by attaching them to Vue.prototype.
- A library that provides an API of its own, while at the same time injecting some combination of the above.
OK, OK. Enough prelude. Let’s write some code!
What we’re making
At Spektrum, Snipcart’s mother agency, our designs go through an approval process, as I’m sure is typical at most other shops and companies. We allow a client to comment and make suggestions on designs as they review them so that, ultimately, we get the green light to proceed and build the thing.
We generally use InVision for all this. The commenting system is a core component in InVision. It lets people click on any portion of the design and leave a comment for collaborators directly where that feedback makes sense. It’s pretty rad.
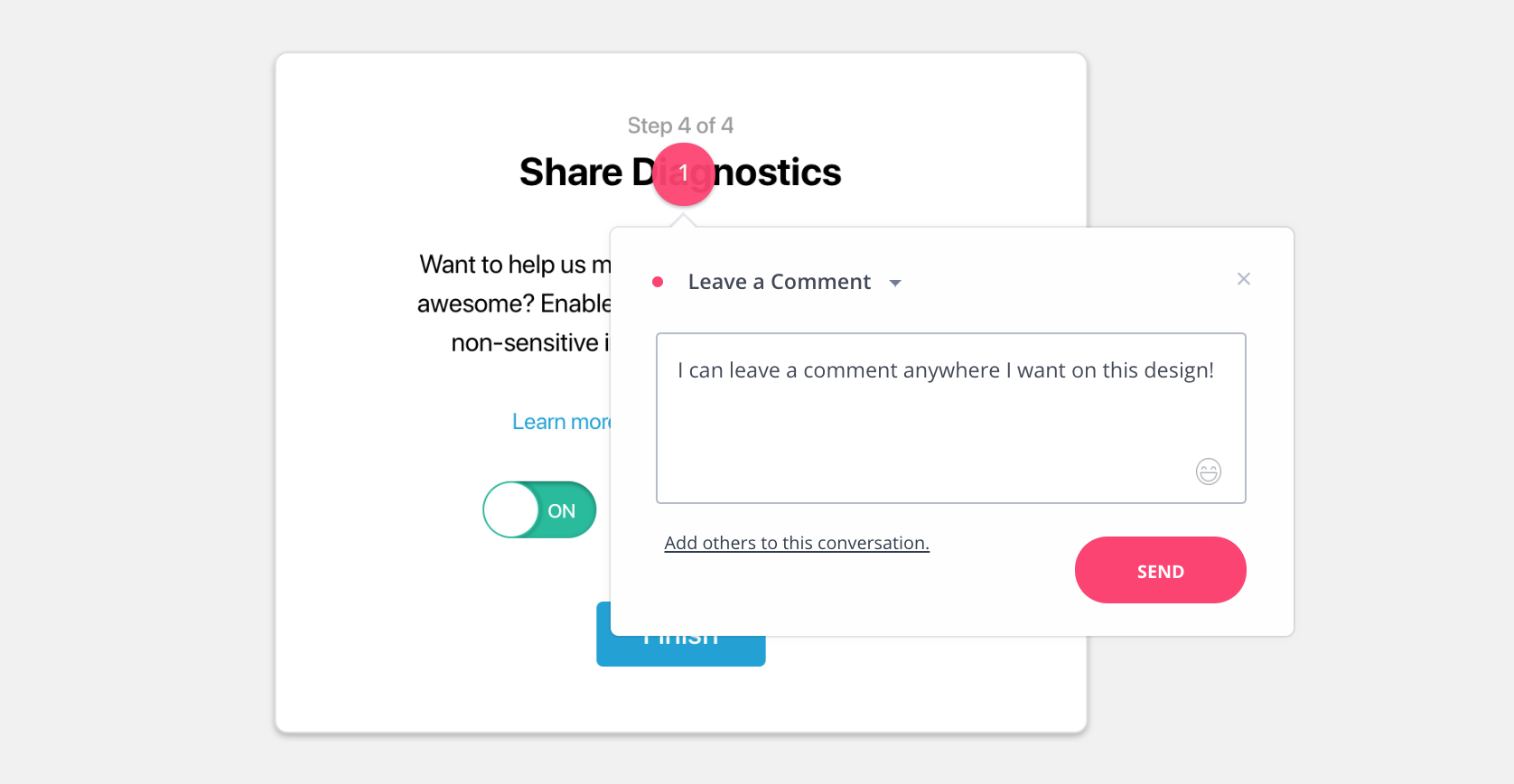
As cool as InVision is, I think we can do the same thing ourselves with a little Vue magic and come out with a plugin that anyone can use as well.
The good news here is they’re not that intimidating. A basic knowledge of Vue is all you need to start fiddling with plugins right away.
Step 1. Prepare the codebase
A Vue plugin should contain an install method that takes two parameters:
- The global
Vueobject - An object incorporating user-defined options
Firing up a Vue project is super simple, thanks to Vue CLI 3. Once you have that installed, run the following in your command line:
$ vue create vue-comments-overlay
# Answer the few questions
$ cd vue-comments-overlay
$ npm run serveThis gives us the classic “Hello World” start we need to crank out a test app that will put our plugin to use.
Step 2. Create the plugin directory
Our plugin has to live somewhere in the project, so let’s create a directory where we can cram all our work, then navigate our command line to the new directory:
$ mkdir src/plugins
$ mkdir src/plugins/CommentsOverlay
$ cd src/plugins/CommentsOverlayStep 3: Hook up the basic wiring
A Vue plugin is basically an object with an install function that gets executed whenever the application using it includes it with Vue.use().
The install function receives the global Vue object as a parameter and an options object:
// src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/index.js
//
export default {
install(vue, opts){
console.log('Installing the CommentsOverlay plugin!')
// Fun will happen here
}
}Now, let’s plug this in our “Hello World” test app:
// src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import CommentsOverlay from './plugins/CommentsOverlay' // import the plugin
Vue.use(CommentsOverlay) // put the plugin to use!
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({ render: createElement => createElement(App)}).$mount('#app')Step 4: Provide support for options
We want the plugin to be configurable. This will allow anyone using it in their own app to tweak things up. It also makes our plugin more versatile.
We’ll make options the second argument of the install function. Let’s create the default options that will represent the base behavior of the plugin, i.e. how it operates when no custom option is specified:
// src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/index.js
const optionsDefaults = {
// Retrieves the current logged in user that is posting a comment
commenterSelector() {
return {
id: null,
fullName: 'Anonymous',
initials: '--',
email: null
}
},
data: {
// Hash object of all elements that can be commented on
targets: {},
onCreate(created) {
this.targets[created.targetId].comments.push(created)
},
onEdit(editted) {
// This is obviously not necessary
// It's there to illustrate what could be done in the callback of a remote call
let comments = this.targets[editted.targetId].comments
comments.splice(comments.indexOf(editted), 1, editted);
},
onRemove(removed) {
let comments = this.targets[removed.targetId].comments
comments.splice(comments.indexOf(removed), 1);
}
}
}Then, we can merge the options that get passed into the install function on top of these defaults:
// src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/index.js
export default {
install(vue, opts){
// Merge options argument into options defaults
const options = { ...optionsDefaults, ...opts }
// ...
}
}Step 5: Create an instance for the commenting layer
One thing you want to avoid with this plugin is having its DOM and styles interfere with the app it is installed on. To minimize the chances of this happening, one way to go is making the plugin live in another root Vue instance, outside of the main app’s component tree.
Add the following to the install function:
// src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/index.js
export default {
install(vue, opts){
...
// Create plugin's root Vue instance
const root = new Vue({
data: { targets: options.data.targets },
render: createElement => createElement(CommentsRootContainer)
})
// Mount root Vue instance on new div element added to body
root.$mount(document.body.appendChild(document.createElement('div')))
// Register data mutation handlers on root instance
root.$on('create', options.data.onCreate)
root.$on('edit', options.data.onEdit)
root.$on('remove', options.data.onRemove)
// Make the root instance available in all components
vue.prototype.$commentsOverlay = root
...
}
}Essential bits in the snippet above:
- The app lives in a new
divat the end of thebody. - The event handlers defined in the
optionsobject are hooked to the matching events on the root instance. This will make sense by the end of the tutorial, promise. - The
$commentsOverlayproperty added to Vue’s prototype exposes the root instance to all Vue components in the application.
Step 6: Make a custom directive
Finally, we need a way for apps using the plugin to tell it which element will have the comments functionality enabled. This is a case for a custom Vue directive. Since plugins have access to the global Vue object, they can define new directives.
Ours will be named comments-enabled, and it goes like this:
// src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/index.js
export default {
install(vue, opts){
...
// Register custom directive tha enables commenting on any element
vue.directive('comments-enabled', {
bind(el, binding) {
// Add this target entry in root instance's data
root.$set(
root.targets,
binding.value,
{
id: binding.value,
comments: [],
getRect: () => el.getBoundingClientRect(),
});
el.addEventListener('click', (evt) => {
root.$emit(`commentTargetClicked__${binding.value}`, {
id: uuid(),
commenter: options.commenterSelector(),
clientX: evt.clientX,
clientY: evt.clientY
})
})
}
})
}
}The directive does two things:
- It adds its target to the root instance’s data. The key defined for it is
binding.value. It enables consumers to specify their own ID for target elements, like so :<img v-comments-enabled="imgFromDb.id" src="imgFromDb.src" />. - It registers a
clickevent handler on the target element that, in turn, emits an event on the root instance for this particular target. We’ll get back to how to handle it later on.
The install function is now complete! Now we can move on to the commenting functionality and components to render.
Step 7: Establish a “Comments Root Container” component
We’re going to create a CommentsRootContainer and use it as the root component of the plugin’s UI. Let’s take a look at it:
<!--
src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/CommentsRootContainer.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<comments-overlay
v-for="target in targets"
:target="target"
:key="target.id">
</comments-overlay>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CommentsOverlay from "./CommentsOverlay";
export default {
components: { CommentsOverlay },
computed: {
targets() {
return this.$root.targets;
}
}
};
</script>What’s this doing? We’ve basically created a wrapper that’s holding another component we’ve yet to make: CommentsOverlay. You can see where that component is being imported in the script and the values that are being requested inside the wrapper template (target and target.id). Note how the target computed property is derived from the root component’s data.
Now, the overlay component is where all the magic happens. Let’s get to it!
Step 8: Make magic with a “Comments Overlay” component
OK, I’m about to throw a lot of code at you, but we’ll be sure to walk through it:
<!-- src/plugins/CommentsOverlay/CommentsRootContainer.vue -->
<template>
<div class="comments-overlay">
<div class="comments-overlay__container" v-for="comment in target.comments" :key="comment.id" :style="getCommentPostition(comment)">
<button class="comments-overlay__indicator" v-if="editing != comment" @click="onIndicatorClick(comment)">
{{ comment.commenter.initials }}
</button>
<div v-else class="comments-overlay__form">
<p>{{ getCommentMetaString(comment) }}</p>
<textarea ref="text" v-model="text" />
<button @click="edit" :disabled="!text">Save</button>
<button @click="cancel">Cancel</button>
<button @click="remove">Remove</button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="comments-overlay__form" v-if="this.creating" :style="getCommentPostition(this.creating)">
<textarea ref="text" v-model="text" />
<button @click="create" :disabled="!text">Save</button>
<button @click="cancel">Cancel</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['target'],
data() {
return {
text: null,
editing: null,
creating: null
};
},
methods: {
onTargetClick(payload) {
this._resetState();
const rect = this.target.getRect();
this.creating = {
id: payload.id,
targetId: this.target.id,
commenter: payload.commenter,
ratioX: (payload.clientX - rect.left) / rect.width,
ratioY: (payload.clientY - rect.top) / rect.height
};
},
onIndicatorClick(comment) {
this._resetState();
this.text = comment.text;
this.editing = comment;
},
getCommentPostition(comment) {
const rect = this.target.getRect();
const x = comment.ratioX <em> rect.width + rect.left;
const y = comment.ratioY <em> rect.height + rect.top;
return { left: `${x}px`>, top: `${y}px` };
},
getCommentMetaString(comment) {
return `${
comment.commenter.fullName
} - ${comment.timestamp.getMonth()}/${comment.timestamp.getDate()}/${comment.timestamp.getFullYear()}`;
},
edit() {
this.editing.text = this.text;
this.editing.timestamp = new Date();
this._emit("edit", this.editing);
this._resetState();
},
create() {
this.creating.text = this.text;
this.creating.timestamp = new Date();
this._emit("create", this.creating);
this._resetState();
},
cancel() {
this._resetState();
},
remove() {
this._emit("remove", this.editing);
this._resetState();
},
_emit(evt, data) {
this.$root.$emit(evt, data);
},
_resetState() {
this.text = null;
this.editing = null;
this.creating = null;
}
},
mounted() {
this.$root.$on(`commentTargetClicked__${this.target.id}`, this.onTargetClick
);
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.$root.$off(`commentTargetClicked__${this.target.id}`, this.onTargetClick
);
}
};
</script>I know, I know. A little daunting. But it’s basically only doing a few key things.
First off, the entire first part contained in the <template> tag establishes the markup for a comment popover that will display on the screen with a form to submit a comment. In other words, this is the HTML markup that renders our comments.
Next up, we write the scripts that power the way our comments behave. The component receives the full target object as a prop. This is where the comments array and the positioning info is stored.
Then, the magic. We’ve defined several methods that do important stuff when triggered:
- Listens for a click
- Renders a comment box and positions it where the click was executed
- Captures user-submitted data, including the user’s name and the comment
- Provides affordances to create, edit, remove, and cancel a comment
Lastly, the handler for the commentTargetClicked events we saw earlier is managed within the mounted and beforeDestroy hooks.
It’s worth noting that the root instance is used as the event bus. Even if this approach is often discouraged, I judged it reasonable in this context since the components aren’t publicly exposed and can be seen as a monolithic unit.
Aaaaaaand, we’re all set! After a bit of styling (I won’t expand on my dubious CSS skills), our plugin is ready to take user comments on target elements!
Getting acquainted with more Vue plugins
We spent the bulk of this post creating a Vue plugin but I want to bring this full circle to the reason we use plugins at all. I’ve compiled a short list of extremely popular Vue plugins to showcase all the wonderful things you gain access to when putting plugins to use.
- Vue-router – If you’re building single-page applications, you’ll without a doubt need Vue-router. As the official router for Vue, it integrates deeply with its core to accomplish tasks like mapping components and nesting routes.
- Vuex – Serving as a centralized store for all the components in an application, Vuex is a no-brainer if you wish to build large apps with high maintenance.
- Vee-validate – When building typical line of business applications, form validation can quickly become unmanageable if not handled with care. Vee-validate takes care of it all in a graceful manner. It uses directives, and it’s built with localization in mind.
I’ll limit myself to these plugins, but know that there are many others waiting to help Vue developers, like yourself!
And, hey! If you can’t find a plugin that serves your exact needs, you now have some hands-on experience crafting a custom plugin. ?
Source: CSS-tricks.com