Almost every week we get to see a new tool or product being released for GraphQL development. Yeah, that’s how hot the GraphQL ecosystem is currently is. Today, we’ll be looking at one of the tools, which is Prisma. We’ll be looking at how to get started with Prisma.
Prerequisites
To follow along, this tutorial assumes the following:
- Node.js and NPM installed on your computer
- Basic knowledge of GraphQL
What’s Prisma
Prisma is a data layer that turns a database into a GraphQL API.
We can look at it as a kind of ORM, but it’s much more powerful than traditional ORMs.
With Prisma, we get a server (Prisma server) that act as a proxy for our database and a high-performance query engine that runs on the server, which generates actual database queries for us. In addition to these, we also get a client (Prisma client), which we can use to interact with the server. Prisma also adds realtime event system to our database, so we can subscribe to database events in realtime.
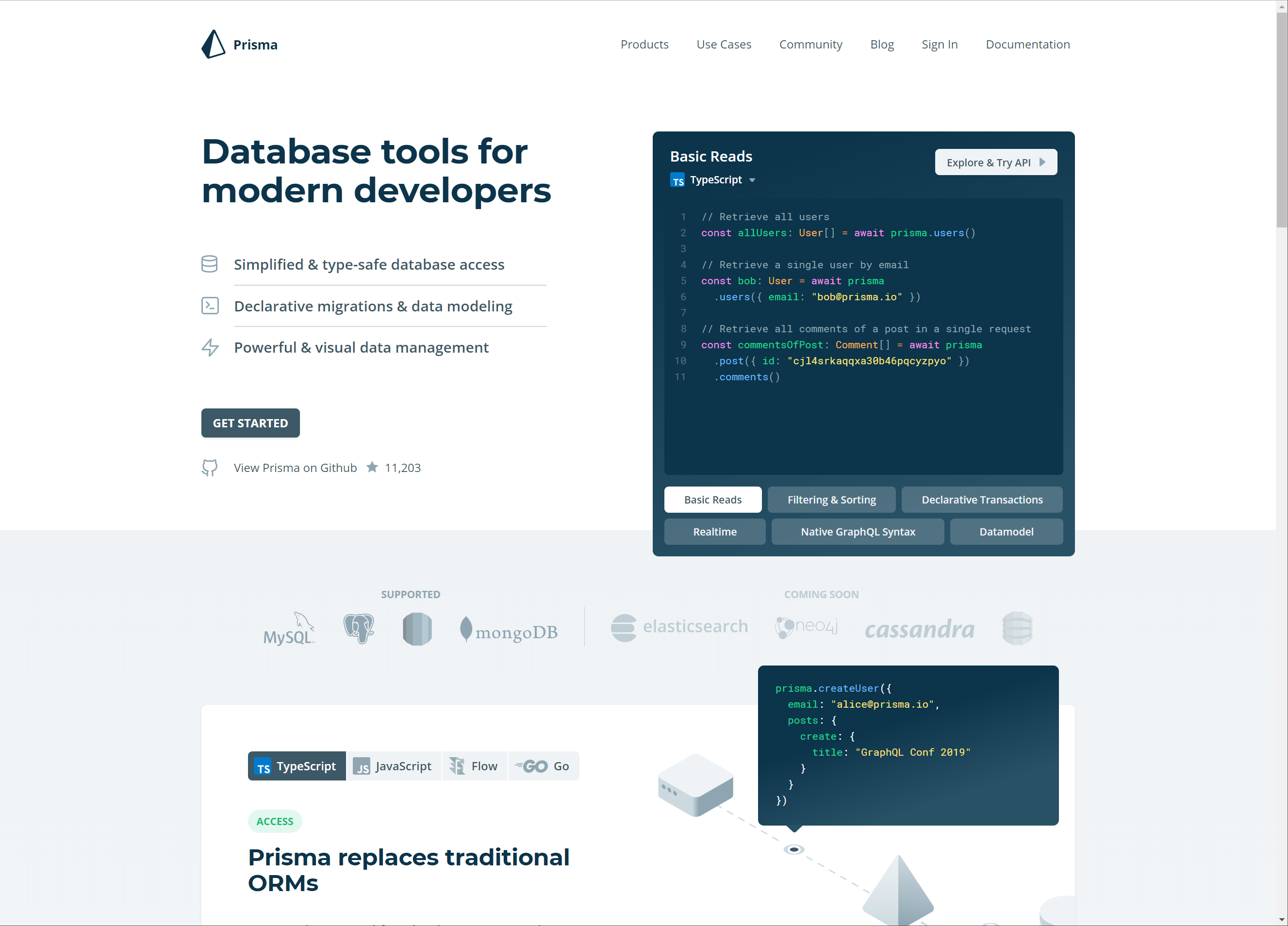
Prisma works with both new and existing databases. In the case of an existing database, Prisma will generate the datamodel based on the database schema.
To learn about what Prisma is and why you should use it, do checkout the their official docs.
Overview of How it Works
Having seen what Prisma is, let’s take an overview look of how it works.
With a New Database
First, let’s look at how it works with a new database:
- Create a new Prisma service
- Set up and connect Prisma with your database
- Define the datamodel
- Deploy the Prisma API
- Generate the Prisma client for your programming language of choice
- Create a GraphQL server that uses the Prisma client to interact with your database
With an Existing Database
Now, let’s see how it works with an existing database:
- Create a new Prisma service
- Set up and connect Prisma with your existing database, using the Prisma Docker image
- Generate the datamodel from your database schema
- Deploy the Prisma API
- Generate the Prisma client for your programming language of choice
- Create a GraphQL server that uses the Prisma client to interact with your database
Note: To use Prisma locally, you need to have Docker installed on your machine. Note: Using an existing database with Prisma currently only works when using PostgreSQL databases.
Getting Started
To get started with Prisma, we need to install the Prisma CLI. There are a couple of ways to install the CLI, but we’ll be installing it using npm:
$ npm install -g prismaWith the CLI installed, we can start using it. We’ll use it to create a new Prisma service:
$ prisma init scotch-task-managerChoose Demo server from the prompt to use an hosted demo server that already has database included, then we’ll be redirected to log in (or sign up if we don’t have an account yet) to Prisma Cloud and grant the CLI permissions to our account.
Note: Because we are using the demo server, which is hosted on Prisma cloud, hence the need of the Prisma cloud account. It is not required we have an account with Prisma cloud before we can use Prisma.
Back to the terminal, choose any of the provided region of the demo server. Then choose the defaults for both the name for our service and the name for our stage, that is, scotch-task-manager and dev respectively. Lastly, select Prisma JavaScript Client as the programming language for the generated Prisma client.
This will create two files: datamodel.prisma and prisma.yml inside the project directory. Also, a Prisma client will be auto-generated. We’ll go through these files shortly.
Based on the types defined inside datamodel.prisma, a GraphQL API is exposed with CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) and realtime operations. This API is called the Prisma API.
Now, let’s deploy our newly created Prisma API:
$ cd scotch-task-manager
$ prisma deployThis will deploy the default User type that Prisma created for us to our selected region. It will also display the live endpoints (HTTP and Websocket. We are only interested in HTTP in this tutorial) for our Prisma GraphQL database.
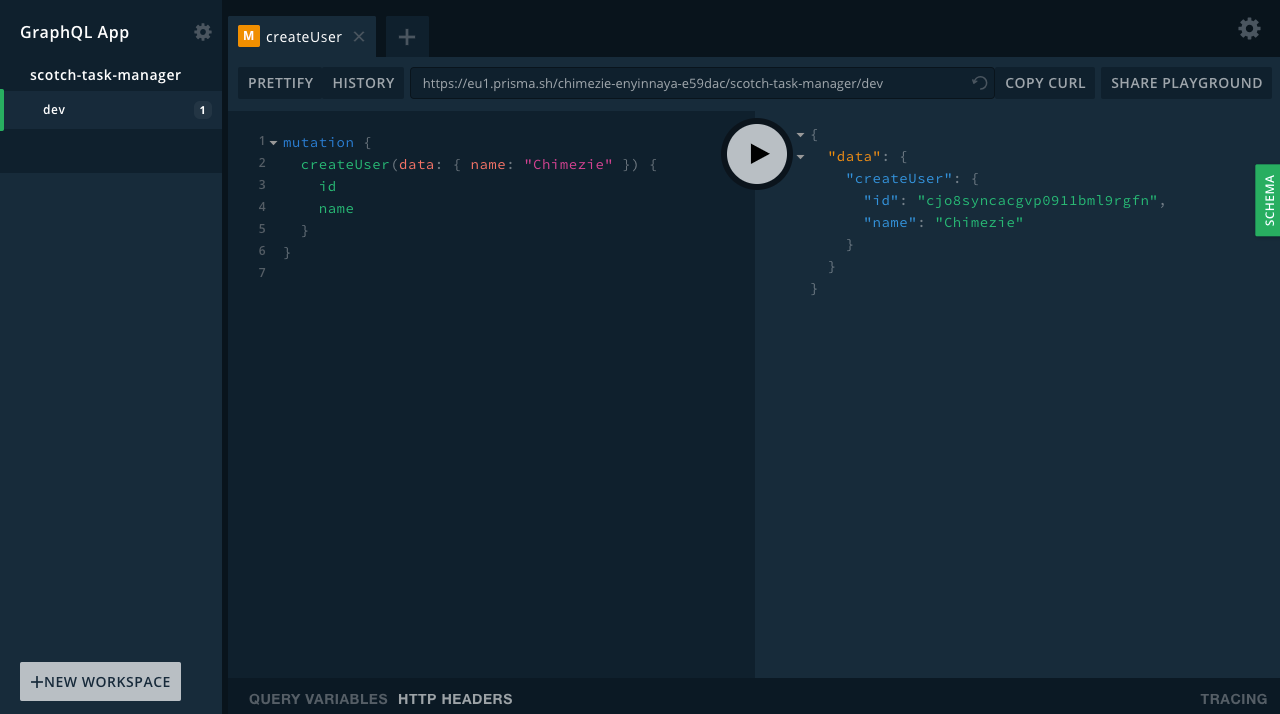
Now, we can take our new Prisma API for a spin in the GraphQL Playground:
$ prisma playgroundWhich we can access at http://localhost:3000/playground. So let’s create a new user with the following mutation:
mutation {
createUser(data: { name: "Chimezie" }) {
id
name
}
}
Understanding the Prisma files
Before we dive deep into building the GraphQL server for our app, let’s quickly go through the files Prisma generated for us.
prisma.yml: This is the configuration file for Prisma. It contains everything that’s required to set up a Prisma service.datamodel.priama: Specifies the datamodel for our application that will be mapped to the database. In other words, it is used to define our database schema.generated/prisma-client: Contains the auto-generated Prisma client library, which can be used to interact with the Prisma API.
Creating a GraphQL server
If all our GraphQL API will do is perform basic CRUD operations, then we would be fine with just the GraphQL API Prisma generated for us. In most cases we would want more than that, so we need to create a GraphQL server to handle our domain-specific logic as well as integrate with third-party services.
We’ll be using the graphql-yoga to create our GraphQL server. So let’s install it along with the other dependency we’ll be needing:
$ yarn add graphql-yoga prisma-client-libprisma-client-lib is needed to run the Prisma client that was generated for us.
Once that’s done installing, create a new directory called src directly within the project’s root directory.
$ mkdir srcThen let’s move the generated directory inside the src directory:
$ mv generated srcNext, within the src directory, create a new file called index.js:
$ cd src
$ touch index.jsThen add the following code to it:
// src/index.js
const { prisma } = require('./generated/prisma-client')
const { GraphQLServer } = require('graphql-yoga')
const resolvers = require('./resolvers')
const server = new GraphQLServer({
typeDefs: './src/schema.graphql',
resolvers,
context: {
prisma
}
})
server.start(() => console.log('Server is running on http://localhost:4000'))We import the Prisma client, graphql-yoga and our resolver functions (we’ll create in a moment). Then we create a new GraphQL server, passing to it our schema (we’ll create this in a moment), the resolver functions and lastly the context, which contains the Prisma client. We pass the Prisma client to the context so that we’ll be able to use it inside our resolver functions. Finally, we start the GraphQL server.
Updating the datamodel
Let’s define the datamodel of our app. The app will be made up of two types: Project and Task. So update datamodel.prisma as below:
# datamodel.prisma
type Project {
id: ID! @unique
name: String!
tasks: [Task!]!
}
type Task {
id: ID! @unique
title: String!
project: Project!
isCompleted: Boolean! @default(value: "false")
}The Project type has three fields; the ID of the project, the name of the project and lastly the project’s tasks. We use the @unique directive on the id field because we want it to be unique for each project and will be set as the primary key on the database table. All the fields are required (denoted with !). The tasks field will return a list of tasks that makes up the project because it is enclosed in []. Notice it has two !, which means the list of tasks can not contain null, but the whole list can be empty.
The Task type is similar to the Project type. It has a project field, which will be the particular project the task belongs to. Then a isCompleted field, which indicates whether a task has been completed or not. We give the field a default value of false using the @default directive.
Note: The default value must always be in double quotes, even for non-string types such as Boolean or Int.
With our datamodel, Project and Type have a one-to-many relationship. A project can have many tasks (because of the tasks field on the Project type) and a task belongs to a project (again, because of the project field on the Task type).
Tips: It is required to use the @relation directive to define a relation when a relation is ambiguous.
For the changes on our datamodel to take effect, we need to redeploy the Prisma API:
$ prisma deployWarning: If you get this warning You already have nodes for this model. This change will result in data loss. for the User type. This is because we created a user earlier and now we don’t need the User type anymore. So we just need to force the deploy: $ prisma deploy –force.
Also, we need to regenerate the Prisma client. We can do that by running the command below:
$ prisma generateDefining the schema
Now let’s start defining the schema that would make up our GraphQL API. Within the src directory, create a new file called schema.graphql:
$ touch schema.graphqlThen add the following code in the newly created file:
# src/schema.graphql
type Query {
projectById(projectId: ID!): Project
completedTasks: [Task!]!
}
type Mutation {
createProject(name: String!): Project
createTask(title: String!, projectId: ID!): Task
markTaskAsCompleted(taskId: ID!): Task
}
type Project {
id: ID!
name: String!
tasks: [Task!]!
}
type Task {
id: ID!
title: String!
project: Project!
isCompleted: Boolean!
}We define a queries to fetch a project by its ID and fetch tasks that have been marked as completed respectively. Also, we define the mutations to create a new project, a new task and to mark a task as completed. Finally, we define the schema for the types in our datamodel.
Tips: Redefining the schema for the types in the datamodel can be redundant and not easily maintainable most especially for large projects. To avoid redefining them, we can use tools like https://github.com/prisma/graphql-import.
Creating the resolver functions
With the schema defined, let’s create the resolver functions that would handle them. Inside the src directory, create a new file called resolvers.js and add the following code in it:
// src/resolvers.js
const resolvers = {
Query: {
projectById (root, { projectId }, { prisma }) {
return prisma.project({ id: projectId })
},
completedTasks (root, args, { prisma }) {
return prisma.tasks({ where: { isCompleted: true } })
}
},
Mutation: {
createProject (root, { name }, { prisma }) {
return prisma.createProject({ name })
},
createTask (root, { title, projectId }, { prisma }) {
return prisma.createTask({
title,
project: { connect: { id: projectId } }
})
},
markTaskAsCompleted (root, { taskId }, { prisma }) {
return prisma.updateTask({
where: { id: taskId },
data: { isCompleted: true }
})
}
},
Project: {
tasks (root, args, { prisma }) {
return prisma.project({ id: root.id }).tasks()
}
},
Task: {
project (root, args, { prisma }) {
return prisma.task({ id: root.id }).project()
}
}
}
module.exports = resolversWe start by creating the resolver functions for the queries. Remember we passed the Prisma client to the context, so we extract it from the context and use it to interact with the Prisma API. The projectById() simply returns the project whose ID matches the supplied project ID. The completedTasks() does pretty the same, but instead it returns a list of tasks that have been marked as completed (that is, isCompleted is true).
If we peep into the generated Prisma client, we’ll see that CRUD operations have been generated for us. So all we need to do is use them. The createProject() calls the createProject() on the Prisma client, which accepts the data we want to insert, in our case just the name of the project since the project’s ID will be auto-generated for us. In the same vein, the createTask() uses the createTask() on the Prisma client, but in addition to the data to be inserted, we connect the task to the project (through the supplied project ID) it belongs to. The markTaskAsCompleted() simply updates a task by setting isCompleted to true. It uses the updateTask(), which accepts two arguments: a where clause to get the task to be updated and the data to update it with.
Lastly, we to create the resolver functions to fetch the custom fields (tasks and project) on the types on our schema.
Tips: Use the singular form of a model to query for a single object and use the plural form of the model to query for a list of objects. E.g. You will notice we are using the singular form of Project to fetch a single project prisma.project({ id: projectId }) and the plural form of Task to fetch a list of tasks prisma.tasks({ where: { isCompleted: true } }).
Testing it out
Now we can test out our app. First, let’s start the GraphQL server:
$ node src/index.jsThe server should be up and running at http://localhost:4000 and opening it will load up the GraphQL Playground.
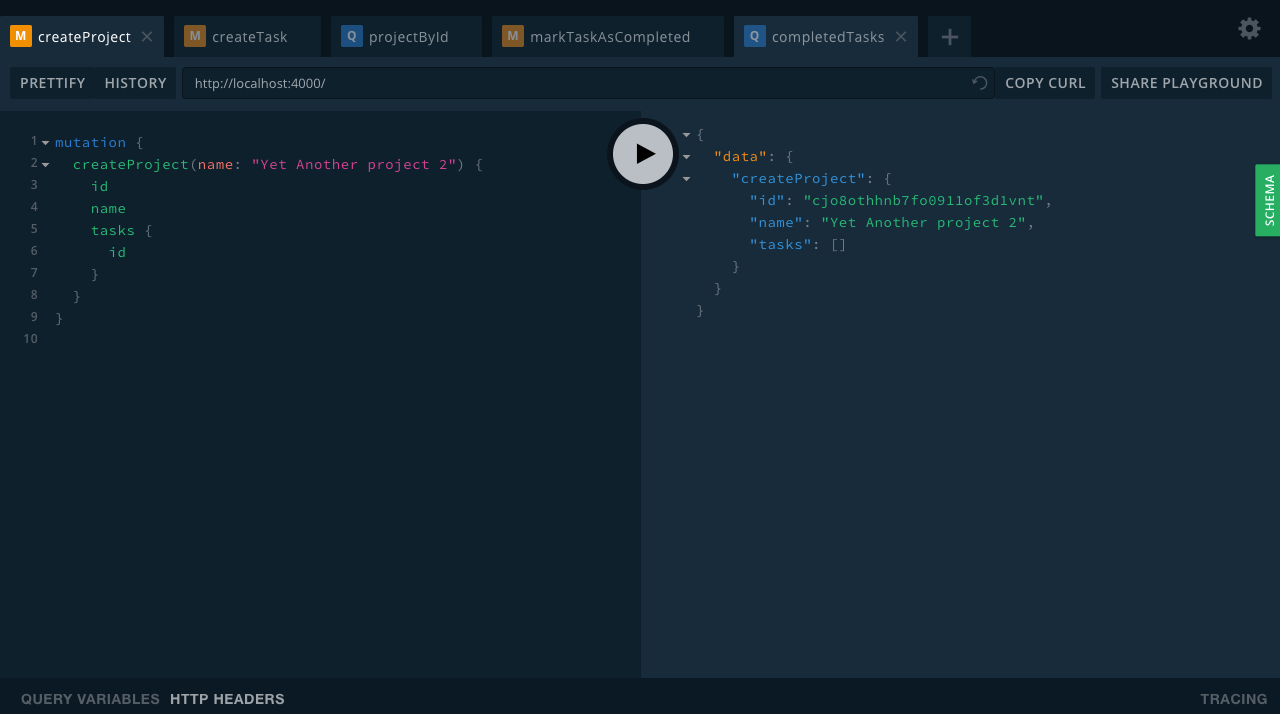
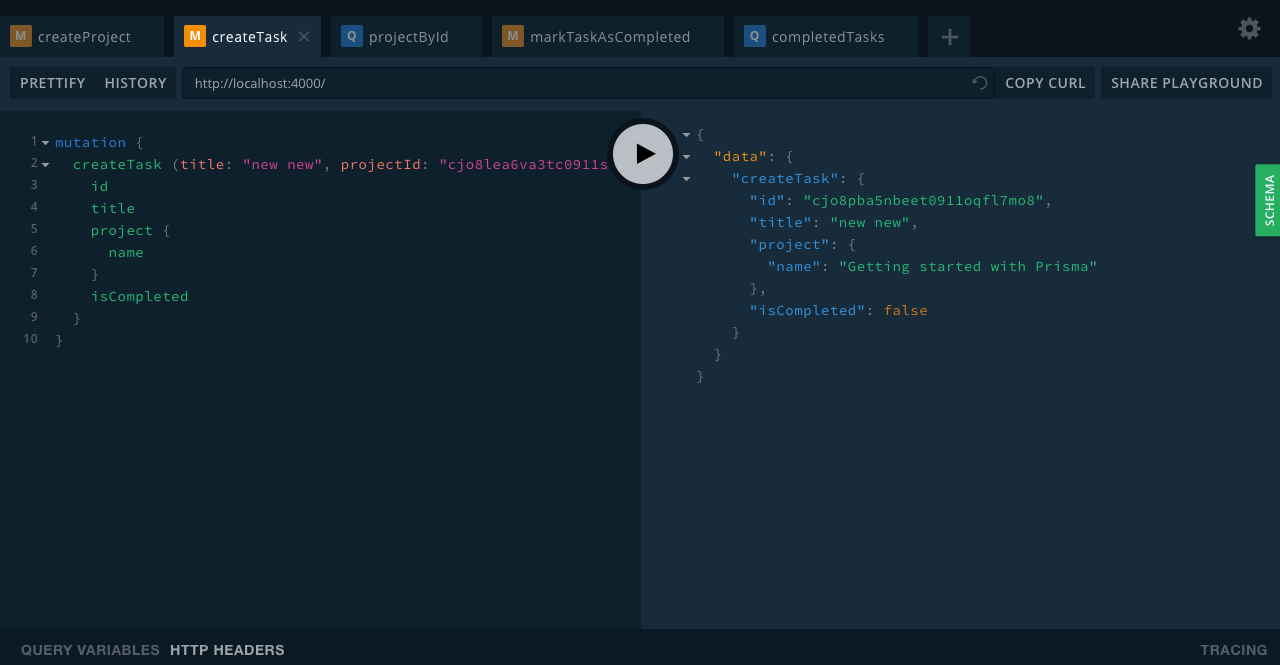
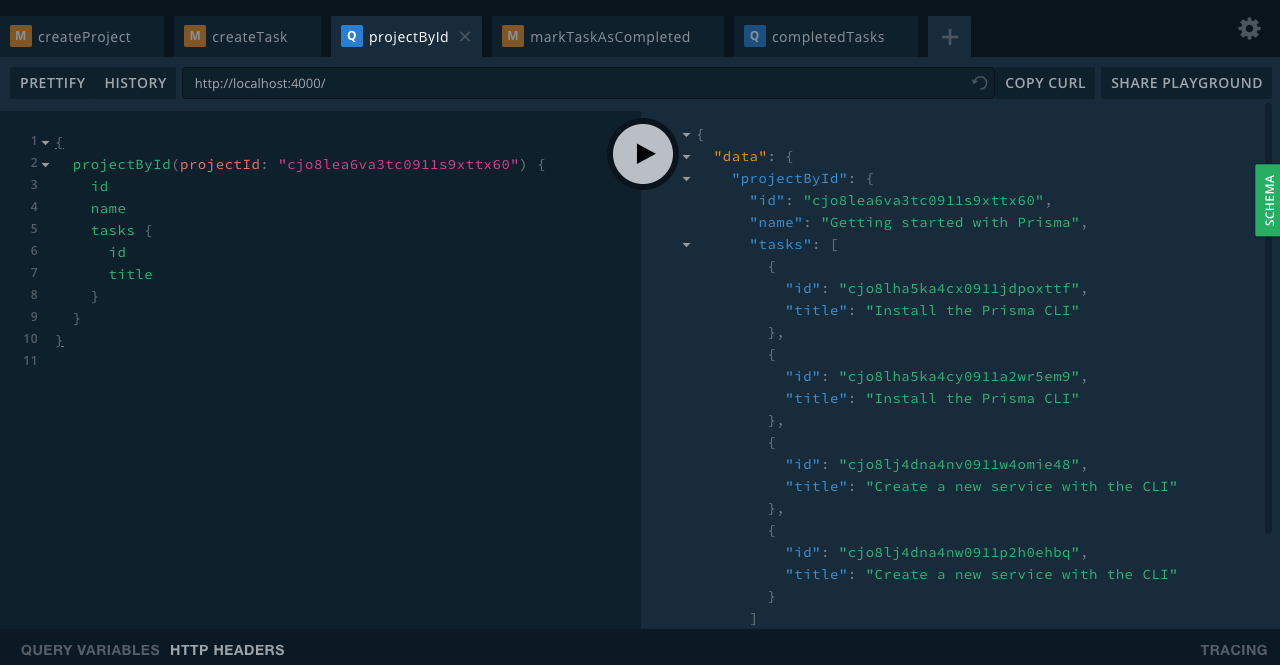
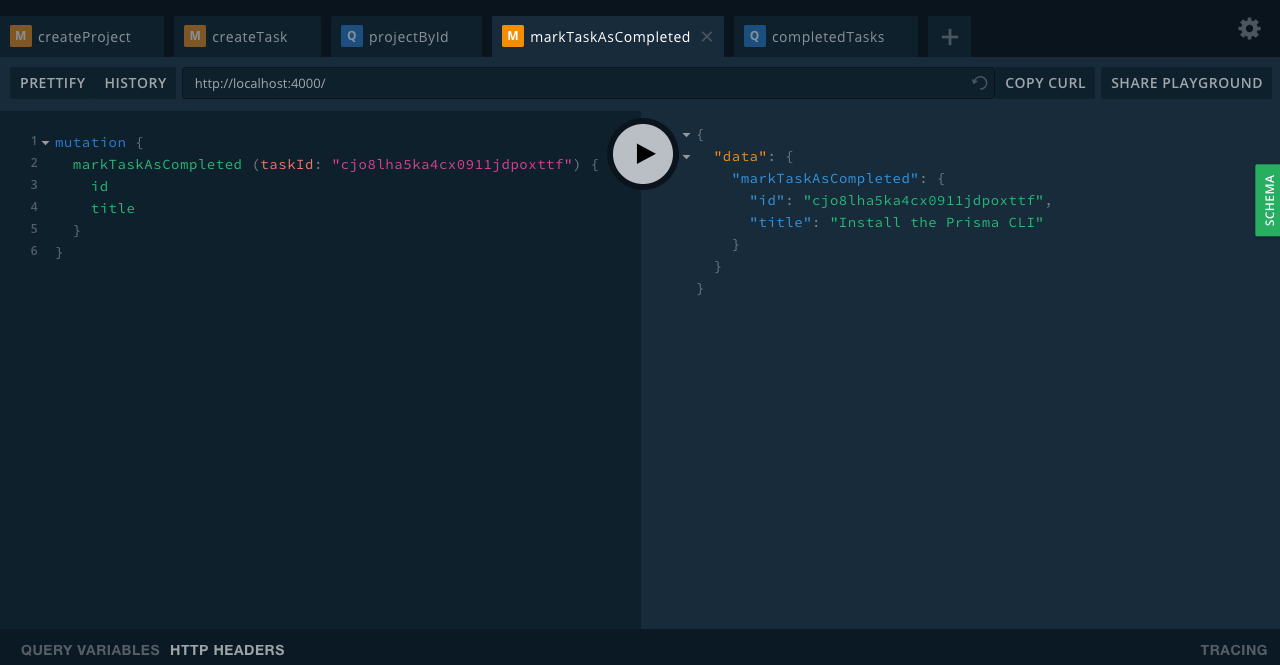
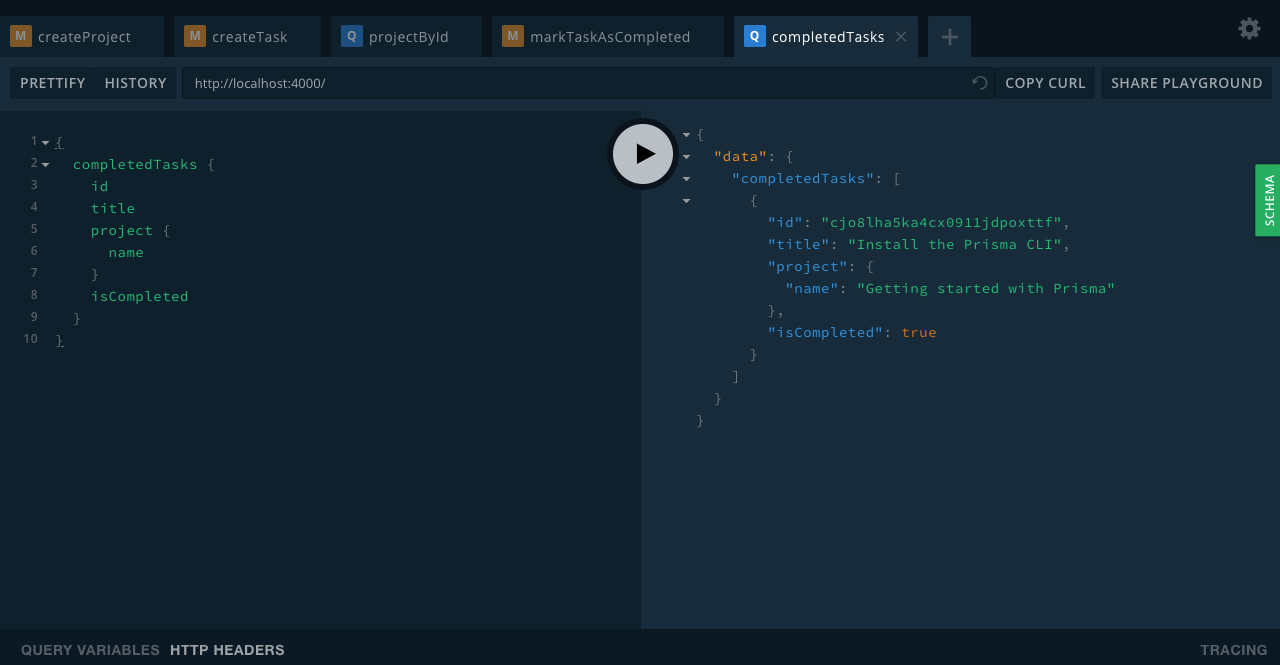
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we looked at what Prisma is, then we looked at how to get started with it by building a GraphQL server. We also looked at how to test our GraphQL server using the GraphQL Playground. If you would like to learn more about Prisma, do check out the docs.
Source: Scotch.io